Introduction
Irrigation is a socio-cultural society system that dynamically depend on the environmental conditions.1 In this early information era, the environment conditions are change rapidly because of rapid development of information technology, globalization and democratization.2 Social and political reforms in 1998 had caused paradigm shift in the irrigation sector.3 The reformation demand that the management of irrigation need to be done in a transparent, responsible, and equitable ways. To achieve that goal, intangible assets becomes a very important factor. Intangible assets affect the process of management organization4,5 and the performance of company.6,7 The physical development must be accompanied with the non-physical development (intangible).
The problems occured in the management of irrigation systems indicate that intangible assets which consist of moral intelligence, emotional intelligence, creative attitude, institutional culture, and farmers participation are decline,3 whereas the condition of intangible assets were affected by the performance of the irrigation system. Consequently, the study of controlling intangible assets in management irrigation system is very important.
Materials And Methods
Molek irrigation area with 3.98 ha in total is the main canal service area that channel the irrigation drain water from the Bendung Blobo that dam up the Bantas River and got addition from Palaan River. Administratively, Molek Irrigation Area comes under the scope of Kepanjen Office, irrigate the land in Malang district that covering 4 districts such as Kepanjen, Kromengan, Ngajum, and Sumber Pucung.
Geographically, Molek Irrigation Area located in Malang district (112o17’11’’- 122o57’50’’ E and 7 44’56’’- 8 26’36’’ S), approximately 335 m above sea level. Daily rainfall ranges between 0 to 147 mm per day. The location map of Molek irrigation area is presented in Figure 2.
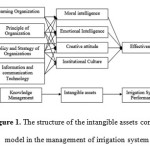 |
Figure 1: The structure of the intangible assets control model in the management of irrigation system. |
 |
Figure 2: The location of Molek irrigation area. |
This research method consists of three stages: model development, collecting data, and testing of models. The controlling model of intangible assets in the management of irrigation system was developed based on Jann knowledge management model.8 The aspects of knowledge management and intangible assets have a vague (fuzzy) value. The knowledge management has four variables, i.e learning organization, principles organization, policies and organization strategies, information and communication technology. The intangible assets have five variables; moral inteligence, emotional intelligence, creative attitude, institutional culture, and farmers participation. Each of knowledge management variable is associated with the variable of intangible assets. The performance of irrigation system is measured by its effectiveness. The performance of irrigation system effectiveness is a ratio of the planting area with the land area. The relationship between the variables is like neural network, so that the control model of intangible assets in the management of irrigation system using the principle of neuro-fuzzy system.9 The structure of intangible assets control model in the management of irrigation system is presented in Figure 1.
The mathematical model relation between knowledge management with the intangible assets is presented in equation 1 to 4:
MI = a LO + b PO + c PS + d ICT + e ….(1)
EI = f LO + g PO + h PS + i ICT + j ….(2)
CA = k LO + l PO + m PS + n ICT + o…(3)
IC = p LO + q PO + r PS + s ICT + t …. (4)
Descriptions:
MI = Moral Intelligence IC = Institutional Culture
EI = Emotional Intelligence CA = Creative Attitude
LO = Learning Organization
PO = Principles Organization PS = Policies and Strategies
ICT = Information and Communication of Technology
a-t = model parameter
The mathematical model relation between intangible assets with the effectiveness of irrigation system is presented in equation 5:
EF = a MI + b EI + c CA + d IC + e …. (5)
Descriptions:
MI = Moral Intelligence IC = Institutional Culture
EI = Emotional Intelligence
CA = Creative Attitude EF = Irrigation Efficiency
a-e = model parameter
The mathematical model that expressed in equations from 1 to 5 are a linear equations. This is due to the research variables are measured from the average value so that the relation between variables is a straight line.
The data collected by questionnaire and personal interviews in March – June 2015. The research subjects are the employees of Water Resources and Irrigation Office of Kepanjen, Malang. The intangible assets, knowledge management is classified into 5 categories based on the normal distribution model which assumed that scores of subjects in the population is normally distributed. The categorization is relative so the wide interval can be determined by researcher within reasonable limits and acceptable reason such as:
X ≤ (µ – 1,5 σ) very poor
(µ – 1,5 σ ) < X ≤ (µ – 0,5 σ) poor
(µ – 0,5 σ ) < X ≤ (µ + 0,5 σ) enough
(µ + 0,5 σ) < X ≤ (µ + 1,5 σ) good
(µ + 1,5 σ) < X very good
The controlling model of intangible assets in the irrigation management system was tested its performance at the Molek irrigation area on Malang, East Java. The model testing measurement was done statistical parameters such as correlation coefficient, Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). The controlling model of intangible assets was tested by comparing between prediction of intangible assets (Aip) model output with the actual intangible assets measurement results. If the correlation coefficient (r) > 0,8 means model has a good performance. The smaller error (MAPE and RMSE) of model performance, the better in result:
The measuring equation of model performance is presented as follows:
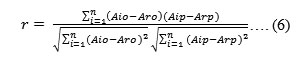
Descriptions:
Aio = Intangible assets observations to i
Aip = Intangible assets prediction to i
Aro = Intangible assets average observation
Arp = Intangible assets average prediction
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE)

Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
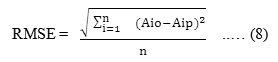
Results and Discussions
The agriculture land follows the patterns of planting seasons; planting season I (PS I), planting season II (PS II), and planting season III (PS III). Each of planting seasons use 4 months period so it is expected that the water availability can be utilized in a fair and equitable way.
Most of residents in the Molek irrigation area worked as farmers. The irrigation management of Molek irrigation area generally in good condition because the farmers can fished throughout the year (except in the downstream of PS III).
Table 1 showed that during planting season (PS I), from upstream to downstream in the agricultural lands of Molek irrigation area are planted with rice, which means land condition at PS I is sufficient with water. Rice also planted at PS II in upstream and middle regions, but in the downstream areas were planted with corn crop. This implies that the PS II irrigation water current began to decline and the water availability is not sufficient in downstream area for rice cultivation.
Table 1: Types of crops under different planting seasons in Molek irrigation areas.
|
Sub Regional Irrigation |
Plant Types |
||
|
PS I (Nov-Feb) |
PS II (Mar-Jun) |
PS III (Jul-Oct) |
|
|
Upstream |
Rice |
Rice |
Rice |
|
Middle |
Rice |
Rice |
Rice |
|
Downstream |
Rice |
Crops |
– |
The farmers in the downstream area use the existing irrigation water for the crops cultivation with rotation system so that the land can beutilized to improve their welfare. At PS III from upstream to the middle of agriculture land in Molek irrigation area also planted with rice, while the downstream area is in fallow condition. This implies that the PS III irrigation water flow decreased and there was no enough water for rice cultivation at downstream area. All farmers in Molek irrigation area (except in the downstream), use the existing irrigation water for rice cultivation with rotation system. The timing and amount of water is determined by Kuwowo, a villager which responsible for managing the irrigation.
The knowledge management of secondary irrigation system which represented by employees of Water Resources and Irrigation of Kepanjen Office, Malang is presented in Table 2.
Table 2.:The knowledge management of secondary irrigation system.
|
Categories |
Learning Org. |
Principles of Org. |
Policies & Strategy |
ICT |
||||
|
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
|
| Very Poor |
18 |
66,7 |
3 |
11,1 |
3 |
11,1 |
21 |
77,8 |
| Poor |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Enough | 9 |
33,3 |
20 |
74,1 |
20 |
74,1 |
6 |
22,2 |
| Good |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Very Good |
0 |
0,0 |
4 |
14,8 |
4 |
14,8 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Total |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
Table 2 showed that 66,7% employees have very poor learning organization level. This implies that the employees are mature person, shared vision, systems of thinking, mental models, and very poor of team learning. Approximately 11.1% employees have a very poor level principles organization. They are less understand about objectives formulation, labor division and delegation of power, authority ranges, levels of supervision, unified command and responsibilities and coordination. Around 33.3% employees have sufficient level of policy and strategy organization. They have a unified and integrated plan linking organizational excellence with environmental challenges, which are designed to ensure that the main organization purpose can be achieved through appropriate implementation by the organization. Most employees (77,8%) have a very poor level of understanding and use of information and communication technology.
Intangible asset of secondary level irrigation system which represented by employees of Kepanjen Water Resources and Irrigation, Malang, consists of moral intelligence, emotional intelligence, creative attitudes, and institutional culture which presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Intangible assets of secondary level irrigation system.
|
Categories/ Intangible Assets |
Moral Intelligence |
Emotional Intelligence |
Creative Attitude |
Institutional Culture |
||||
|
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
Total |
(%) |
|
| Very Poor |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
2 |
7,4 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Poor |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
2 |
7,4 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Enough |
0 |
0,0 |
2 |
7,4 |
3 |
11,1 |
0 |
0,0 |
| Good |
27 |
100,0 |
25 |
92,6 |
20 |
74,1 |
21 |
77,8 |
| Very Good |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
0 |
0,0 |
6 |
22,2 |
| Total |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
27 |
100,0 |
Table 3 showed that all employees (100%) have a good moral intelligence. The employees have a good willingness to integrate the universal values into their behavior, responsible for committed acts and understand the consequence, trying not to harm the others, and compassionate.
Around 92,6% employees have emotional intelligence in good category. Most of employees have a good ability to understand their emotions appropriately and accurately in a variety of situations, managing emotions well, striving to achieve the goals with quite enthusiastic attitude, passion, strong self-confidence, positive thinking and understand the emotion of other action that appear and interact positively with others.
Approximately, 74,8% employees have creative attitude in good category. Most of the employees have a good ability to use their ideas to solve a problem, finding a wide variety of ideas to solve problems outside the usual categories, providing a unique or extraordinary response, and the direction of the idea expressed in detail to make it into reality.
About 77,2% employees have institutional culture in good category. The employees’ behavior of Molek irrigation system in secondary level have been in line with the institution’s goals, decisions are taken by consensus, thinking in order to achieve similar goals, the existence of family relationship, the farmers welfare is a priority that has the spirit of continuous learning progress, reward for achievement employees and making decision based on empirical data. The effectiveness of the secondary level of Molek irrigation area in 2014 is presented in Table 4.
Table 4: Effectiveness of the secondary level of Molek irrigation area in 2014.
|
Categories/ Irrigation System |
Effectiveness |
|
|
Total of Resp. |
Percent (%) |
|
| very poor |
0 |
0,0 |
| poor |
0 |
0,0 |
| enough |
0 |
0,0 |
| good |
1 |
37,0 |
| very good |
26 |
96,3 |
| Total |
27 |
100,0 |
Table 4 showed that the most of the land in the secondary channel services (96,3%) have a very good level of effectiveness. Most of the areas are able to be planted well.
The controlling model of intangible assets in irrigation system management has two sub models; relationship model between knowledge management with intangible assets and relationship model of intangible assets with irrigation system performance.
The relationship between knowledge management consists of a learning organization (LO), the principle of organization (PO), the policy and strategy (PS), information and communication technology (ICT) with intangible assets tertiary level of irrigation system which consist of moral intelligence (MI), emotional intelligence (EI), creative attitude (CA), institutional culture (IC) is expressed in the equation 9-12.
MI = 20,68 + 1,78 LO + 4,49 PO + 10,14 PS + 0,63 ICT ………….. (9)
EI = 13,56 + 0,73 LO + 4,82 PO + 7,29 PS – 0,80 ICT …………. (10)
CA = 14,49 + 1,67 LO + 4,51 PO + 5,25 PS – 2,13 ICT ………… (11)
IC = 102,09 + 2,96 LO – 9,47 PO + 18,05 PS – 6,42 ICT …………. (12)
Table 4 showed that the correlation coefficient (r) between intangible assets predictions with actual intangible assets value at 0,67-0,89. This implies that the relationship between predictions intangible assets with actual intangible assets is strong. The error model in predicting intangible assets have a small value which indicated by MAPE (0,06-0,12) and MRSE value (2,21-4,38). MAPE value showed the deviation of the actual data against the average. The smaller of RMSE value indicates good score (Table 5).
Table 5: The result of testing knowledge management relationship model with intangible assets tertiary level irrigation system.
|
Sub Model |
r |
MAPE |
RMSE |
| Knowledge Management – Moral Intelligence |
0,82 |
0,07 |
2,95 |
| Knowledge Management – Emotional Intelligence |
0,86 |
0,06 |
2,21 |
| Knowledge Management – Creative Attitude |
0,89 |
0,06 |
2,31 |
| Knowledge Management – Institutional Culture |
0,67 |
0,12 |
4,38 |
The relation between intangible assets consisting of moral intelligence, emotional intelligence, creative attitudes, cultural institutions with the effectiveness of the irrigation system of secondary level expressed in equation 13.
EF = 0,00002498+0,002143MI+0,001068EI+0,00109CA+0,001008IC … (13)
The correlation coefficient (r) between the effectiveness of irrigation systems predictions with the actual effectiveness of irrigation systems was 0.76, which means that the relationship between the effectiveness of predictions irrigation systems with effectiveness of the actual irrigation system is strong. Error models in predicting the effectiveness of small irrigation systems shown by MAPE value is 0.02 and 0.15 for MRSE. MAPE value showed the deviation data of predictions with actual system, while MRSE indicate deviation data of actual with the value so that the model is adequate.
Conclusion
The present study concluded that the controlling model of intangible assets irrigation systems which built with the principles of neuro-fuzzy can predict the intangible assets and irrigation system performance. This model connects knowledge management, intangible assets, and irrigation system performance. Knowledge management consists of learning organization, principle of organization, policies and strategies of organization, information and communication technology affect the intangible assets irrigaton system. Intangible assests consists of moral intelligence, emotional intelligence, creative attitude, and institutional culture affect the effectiveness of the irrigation system.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Indonesian Directorate General of High Education for research funding granted.
References
- Pusposutardjo S. Persoalan dan Penyelesaian Manajemen Irigasi Yang Berkeadilan. Makalah Seminar Sistem Subak di Bali Menghadapi Era Globalisasi, Denpasar (2004).
- Garvin D. Learning in Action: A Guide to Putting the Learning Organization to Work. Harvard Business School Press, UK (2000).
- Waskitho N.T, Arif S.S., Maksum M., Susanto S. Amortization in Irrigation System Management. Perteta Nasional Seminar, Yogyakarta, (2008).
- Stewart T.A. Intellectual Capital. Doubleday Dell Publishing Group, New York (1999).
- Engstrom T.E.J, Petter W., Siren F.W. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 4(3): 287-303 (2003).
CrossRef - Bontis N. Management Decision, 36(2): 63-76 (1998).
CrossRef - Bontis N., Keow W.C., and Rechardson S. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 1(1): 85-100 (2000).
CrossRef - Tjakraatmadja J.H. Learning 3: Learning Organization and Knowledge Management in Learning Organixation Contex. MSM ITB Progam, Bandung, (2008).
- Kusumadewi S. dan Hartati S. Neuro Fuzzy: Fuzzy System Integration and Neuro Network. Graha Ilmu, Jakarta (2006).
